GraphicsContext
The GraphicsContext object provides methods for drawing images, text and shapes on the canvas.
local dlg = Dialog()
dlg:canvas{
onpaint = function(ev)
local gc = ev.context
-- gc is a GraphicsContext
end
}GraphicsContext.width
local width = gc.widthGets the width of the visible area in pixels. Canvas dimensions change when the dialog is resized by the user.
GraphicsContext.height
local height = gc.heightGets the height of the visible area in pixels. Canvas dimensions change when the dialog is resized by the user.
GraphicsContext.antialias
local aa = gc.antialias
gc.antialias = trueGets or sets whether paths and shapes are painted on using antialiasing.
GraphicsContext.color
local color = gc.color
gc.color = Color(255)Gets or sets the color to paint with the path functions.
GraphicsContext.strokeWidth
local sw = gc.strokeWidth
gc.strokeWidth = 10Gets or sets the width of lines painted when calling GraphicsContext:stroke() or GraphicsContext:strokeRect().
GraphicsContext.blendMode
local bm = gc.blendMode
gc.blendMode = BlendMode.NORMALBlend mode used in stroke(), fill(), drawImage(), etc.
GraphicsContext.opacity
local opacity = gc.opacity
assert(opacity >= 0 and opacity <= 255)
gc.opacity = newOpacityOpacity used in stroke(), fill(), drawImage(), etc.
opacity: 0 completelly transparenty, 255 completelly opaque.
GraphicsContext.theme
It has the same functionality as app.theme, with the only difference that the values returned by accessing dimensions or style metrics data are not affected by the current UI Scale setting. This is useful when you are drawing on a dialog canvas's GraphicsContext with autoScaling enabled, so you don't have to worry about adjusting sizes and measures when painting on the canvas using the current theme.
For instance, when UI Scale is set to 200% this is the difference:
local dlg = Dialog()
dlg:canvas{
onpaint = function(ev)
local b1 = app.theme:styleMetrics("button")
local b2 = ev.context.theme:styleMetrics("button")
print("app.theme: " .. b1.border.top .. " " .. b1.border.left .. " " .. b1.border.bottom .. " " .. b1.border.right)
print("context.theme: " .. b2.border.top .. " " .. b2.border.left .. " " .. b2.border.bottom .. " " .. b2.border.right)
-- Console's output:
-- app.theme: 8 8 12 8
-- context.theme: 4 4 6 4
end
}GraphicsContext:save()
gc:save()Saves the current state of the canvas to restore it later, including:
GraphicsContext:restore()
gc:restore()Restores the last saved canvas state.
GraphicsContext:clip()
gc:clip()Sets the current path as a clipping area for following drawing operations.
Warning: The only option to draw paths not clipped after calling GraphicsContext:clip() is restoring a previously saved state.
-- Save state before clipping
gc:save()
-- Create a rectangle and use it as a clipping region
gc:beginPath()
gc:rect(Rectangle(0, 30, 100, 40))
gc:clip()
-- Stroke a circle with width of 4
gc.strokeWidth = 4
gc:beginPath()
gc:roundedRect(Rectangle(10, 10, 80, 80), 50)
gc:stroke()
-- Restore the state
gc:restore()
-- Fill a smaller circle in white
gc.color = Color {r = 255, g = 255, b = 255, a = 255}
gc:beginPath()
gc:roundedRect(Rectangle(20, 20, 60, 60), 30)
gc:fill()GraphicsContext:strokeRect()
gc:strokeRect(rectangle)Paints the edges of the given rectangle with the current color and current width.
GraphicsContext:fillRect()
gc:fillRect(rectangle)Fills the given rectangle with the current color.
GraphicsContext:fillText()
gc:fillText(string, x, y)Draws on the canvas the given text string, at a position specified by the xy-coordinates.
GraphicsContext:measureText()
local size = gc:measureText(string)Returns the size of the given text using the current font.
GraphicsContext:drawImage()
gc:drawImage(image, x, y)
gc:drawImage(image, srcRect, dstRect)
gc:drawImage(image, srcX, srcY, srcW, srcH, dstX, dstY, dstW, dstH)Draws on the canvas the given image.
If given xy-coordinates, the full image will be drawn at the specified position, in it's original scale.
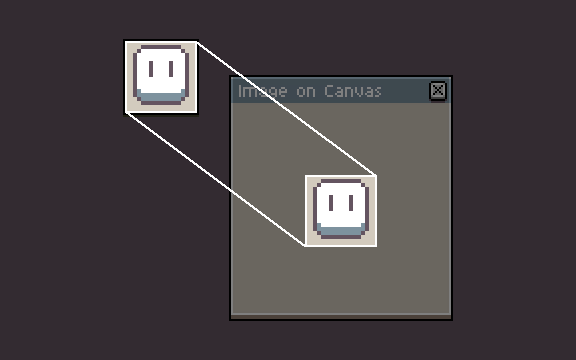
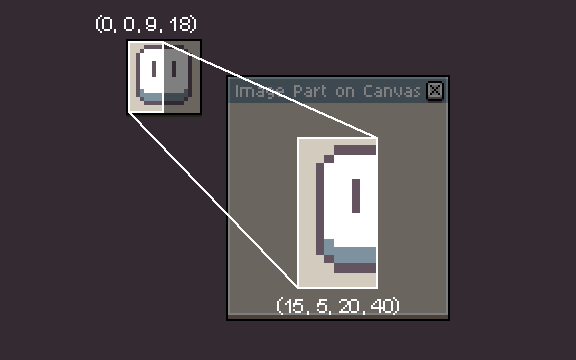
If given source and destination bounds (or their respective values), a part of the image is drawn (specified by the srcRect, or srcX/srcY/srcW/srcH, relative to the image) on the canvas (specified by the dstRect or dstX/dstY/dstW/dstH). This allows drawing only a part of and/or scaling the image.
GraphicsContext:drawThemeImage()
gc:drawThemeImage(partId, point)
gc:drawThemeImage(partId, x, y)Draws on the canvas a theme part specified by the given partId, at a given Point or at specified xy-coordinates.
List of possible parts can be found in theme.xml.
GraphicsContext:drawThemeRect()
gc:drawThemeRect(partId, rectangle)
gc:drawThemeRect(partId, x, y, w, h)Draws on the canvas a theme part specified by the given partId, filling a given Rectangle or at specified xy-coordinates, with given width and height. This method uses nine-slice scaling for parts that have their Slice's center defined.
List of possible parts can be found in theme.xml.
GraphicsContext:beginPath()
gc:beginPath()Starts a new path, emptying the list of tracked sub-paths. This is the first method to call when drawing paths.
GraphicsContext:closePath()
gc:closePath()Closes the current sub-path by connecting the current point with the first point of the current sub-path.
GraphicsContext:moveTo()
gc:moveTo(x, y)Starts a new sub-path at the specified xy-coordinates. This is the second method to call (after GraphicsContext:beginPath()) when drawing paths.
GraphicsContext:lineTo()
gc:lineTo(x, y)Adds a line to the current sub-path, from the last point to the specified xy-coordinates.
Note: This method doesn't draw on the canvas, to draw the path onto the canvas call GraphicsContext:stroke() or GraphicsContext:fill().
GraphicsContext:cubicTo()
gc:cubicTo(cp1x, cp1y, cp2x, cp2y, x, y)Adds a cubic Bézier curve to the current sub-path, from the last point to the specified xy-coordinates, with two control points (specified by cp1x/cp1y and cp2x/cp2y coordinates).
Note: This method doesn't draw on the canvas, to draw the path onto the canvas call GraphicsContext:stroke() or GraphicsContext:fill().
GraphicsContext:oval()
gc:oval(rectangle)Adds an oval enclosed by the given Rectangle to the current sub-path.
Note: This method doesn't draw on the canvas, to draw the path onto the canvas call GraphicsContext:stroke() or GraphicsContext:fill().
GraphicsContext:rect()
gc:rect(rectangle)Adds a given Rectangle to the current sub-path.
Note: This method doesn't draw on the canvas, to draw the path onto the canvas call GraphicsContext:stroke() or GraphicsContext:fill().
GraphicsContext:roundedRect()
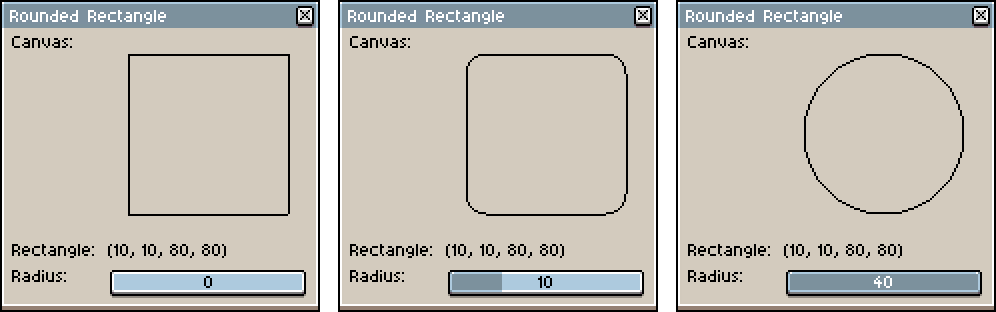
gc:roundedRect(rectangle, r)
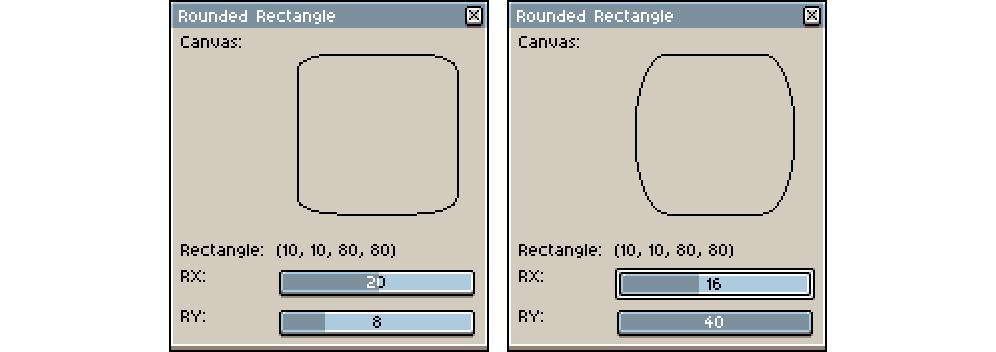
gc:roundedRect(rectangle, rx, ry)Adds a given Rectangle to the current sub-path with rounded corners.
If a single radius is specified, a rectangle with circular corners is created. This method can be used to easily draw circles.
If two radii are specified, a rectangle with elliptical corners is created.
Note: This method doesn't draw on the canvas, to draw the path onto the canvas call GraphicsContext:stroke() or GraphicsContext:fill().
GraphicsContext:stroke()
gc:stroke()Paints the edges of the current path with the current color and current width.
GraphicsContext:fill()
gc:fill()Fills the current path with the current color.